[Win32] [C++] Local RPC over Named Pipe and LPC
Microsoft の分散コンピューティング関連技術は入り乱れていて把握が難しいのが現状です。その中でも外せないのが RPC (=Remote Procedure Call) でしょうか。
- MSRPC = DCE/RPC の MS 実装
- DCOM = MSRPC を使った COM
- COM+ = COM + MTS
- ローカルでの RPC では多くの場合 Windows カーネルが提供する LPC (=Local Procedure Call) が使われる
DCOM じゃない COM のメソッド呼び出しは RPC を使っているのではないかという気がしますが、ちょっと自信がないです。間違っていたら誰かコメント下さい。これもカーネルデバッグすれば分かるのでしょうが。
COM については、以下のページを参考にして下さい。
COM+ (Component Services)
http://www.microsoft.com/com/default.mspx
今回は、ローカルでの RPC を検証するサンプル プログラムを作ってみました。
RPC が対応しているプロトコルの一覧は以下のページにありますが、そのうちの名前付きパイプと LPC を使えるようにしてあります。
Protocol Sequence Constants
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa374395(VS.85).aspx
ベースは、以下のページにあるサンプル プログラムを使っています。(コピペともいう)
RPC Sample Application
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd418893(v=prot.10).aspx
作る順番としては、こんな感じになるでしょうか。全部 Visual Studio からできますが、uuidgen と MIDL をコマンドラインから直接実行する方が面白いです。
- uuidgen で IDL ファイルのひな型を作る
- IDL ファイルと ACF ファイルを書く
- MIDL でコンパイル
- RPC サーバーを書く
- RPC クライアントを書く
- とりあえず動かす
1. uuidgen で IDL ファイルのひな型を作る
IDL (=Interface Definition Language) は、RPC インターフェースを定義するためのプログラミング言語で、Windows に限らず、Linux でも動くコンパイラはあるようです。
スタートメニューから、 “Visual Studio Command Prompt (2010)” を実行し、以下のコマンドを実行します。
> uuidgen /i /opipo.idl
以下のようなひな型が生成されます。要は UUID が生成されただけです。
[
uuid(6504fa96-8126-401b-adfd-18580a6e9d86),
version(1.0)
]
interface INTERFACENAME
{
}
2. IDL ファイルと ACF ファイルを書く
IDL ファイルには、RPC メソッドのスタブを C/C++ のプロトタイプ宣言として記述します。INTERFACENAME も適当なものに変えておきます。今回は 3 つのメソッドを宣言しました。
//
// pipo.idl
//
// generated with 'uuidgen /i /opipo.idl'
// compile with 'midl pipo.idl'
//
// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa367088
//
[
uuid(6504fa96-8126-401b-adfd-18580a6e9d86),
version(1.0)
]
interface pipo
{
void RpcSleep(int Duration);
void Hello([in, string] const wchar_t *String);
void Shutdown();
}
コメントにも入れましたが、以下のページに MIDL のリファレンスがあるので、適宜参照してください。
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa367088
ACF ファイルは、メモリや例外など、メソッドに関する属性を記述するのに使われるファイル、だそうです。
今回は RPC バインディング ハンドルを宣言するのに使います。これを書くことで、ハンドルを自動的に定義/宣言してくれるので楽です。
//
// pipo.acf
//
// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa366717(v=VS.85).aspx
//
[
implicit_handle(handle_t pipo_IfHandle)
]
interface pipo
{
}
3. MIDL でコンパイル
IDL と ACF ファイルをコンパイルします。 2 つのファイルを同じフォルダーにおいて、以下のコマンドを実行して下さい。
> midl pipo.idl
Microsoft (R) 32b/64b MIDL Compiler Version 7.00.0555
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Processing .\pipo.idl
pipo.idl
Processing .\pipo.acf
pipo.acf
これにより、以下 3 つのファイルが生成されますので、これから作るクライアントやサーバー プログラムのプロジェクトにコピーしておきます。
- pipo.h - クライアント/サーバー共通のヘッダー
- pipo_c..c - クライアント用ソース ファイル (スタブの定義など)
- pipo_s.c - サーバー用ソース ファイル
RPC 基盤では、RPC メソッドに渡すパラメーターのメモリ領域を動的に確保/解放するための関数を必要としており、その定義はクライアント/サーバーの双方に自分で書かなけれないけません。関数名は midl_user_allocate と midl_user_free です。とはいっても、malloc と free を呼び出すだけにするのが慣習のようです。もし大きなメモリブロックが必要だったら、VirtualAlloc を使った方がいいかもしれません、たぶん。
4. RPC サーバーを書く
コマンドライン引数を処理して、指定されたプロトコルで待機するだけのプログラムです。
Shutdown は、クライアントからサーバーを終了するためのメソッドで、これを用意しておくのは慣習みたいなので実装しておきました。midl_user_allocate と midl_user_free を定義し忘れると [未解決のシンボル] エラーが出るので注意。もちろん rpcrt4.lib をリンカに追加するのも忘れないように。
//
// piposerver.cpp
//
// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd418893(v=prot.10).aspx
// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa374395(VS.85).aspx
//
#include <Windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pipo.h"
#define PROT_LPC ((RPC_WSTR)L"ncalrpc")
#define PROT_NP ((RPC_WSTR)L"ncacn_np")
void RpcSleep(int Duration) {
wprintf(L"[Pipo:0x%x] Duration: %u msec...\n",
GetCurrentThreadId(), Duration);
Sleep(Duration);
wprintf(L"[Pipo:0x%x] done.\n", GetCurrentThreadId());
}
void Hello(LPCWSTR String) {
wprintf(L"[Pipo:0x%x] %s\n", GetCurrentThreadId(), String);
}
void Shutdown() {
RPC_STATUS Status= RPC_S_OK;
Status= RpcMgmtStopServerListening(NULL);
if ( Status!=RPC_S_OK )
wprintf(L"[Shutdown:0x%x] RpcMgmtStopServerListening failed (0x%08x)\n",
GetCurrentThreadId(), Status);
Status = RpcServerUnregisterIf(NULL, NULL, FALSE);
if ( Status!=RPC_S_OK )
wprintf(L"[Shutdown:0x%x] RpcServerUnregisterIf failed (0x%08x)\n",
GetCurrentThreadId(), Status);
wprintf(L"[Shutdown:0x%x] done.\n", GetCurrentThreadId());
}
void __RPC_FAR * __RPC_USER midl_user_allocate(size_t len) {
return malloc(len);
}
void __RPC_USER midl_user_free(void __RPC_FAR * ptr) {
free(ptr);
}
#define MAX_PROTOCOL 10
static wchar_t upperstr[MAX_PROTOCOL+1];
const wchar_t *ToUpper(const wchar_t *s) {
for ( int i=0 ; i<MAX_PROTOCOL+1 ; ++i ) {
upperstr[i]= toupper(s[i]);
if ( s[i]==0 )
return upperstr;
}
upperstr[MAX_PROTOCOL]= 0;
return upperstr;
}
/*
usage: piposerver [PIPE|LPC] [endpoint] [maxinstance]
*/
int wmain(int argc, wchar_t *argv[]) {
if ( argc<4 ) {
wprintf(L"\nusage: piposerver [PIPE|LPC] [endpoint] [maxinstance]\n");
exit(ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER);
}
LPCWSTR UpperProt= ToUpper(argv[1]);
RPC_WSTR Protocol= NULL;
if ( wcscmp(UpperProt, L"PIPE")==0 )
Protocol= PROT_NP;
else if ( wcscmp(UpperProt, L"LPC")==0 )
Protocol= PROT_LPC;
else {
wprintf(L"Unknown procotol.\n");
return ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER;
}
RPC_STATUS Status= RPC_S_OK;
RPC_WSTR Endpoint= (RPC_WSTR)argv[2];
unsigned int MaxInstance= min(_wtoi(argv[3]),
RPC_C_LISTEN_MAX_CALLS_DEFAULT);
Status = RpcServerUseProtseqEp(Protocol, MaxInstance, Endpoint, NULL);
if ( Status!=RPC_S_OK ) {
wprintf(L"RpcServerUseProtseqEp failed (0x%08x)\n", Status);
exit(Status);
}
Status= RpcServerRegisterIf(pipo_v1_0_s_ifspec, NULL, NULL);
if (Status!=RPC_S_OK) {
wprintf(L"RpcServerRegisterIf failed (0x%08x)\n", Status);
exit(Status);
}
wprintf(L"Protocol: %s\n", Protocol);
wprintf(L"Endpoint: %s\n", Endpoint);
wprintf(L"Max instances: %u\n", MaxInstance);
wprintf(L"RPC Server listeing (TID:0x%x) ...\n\n", GetCurrentThreadId());
Status = RpcServerListen(1, MaxInstance, 0);
if (Status!=RPC_S_OK) {
wprintf(L"RpcServerListen failed (0x%08x)\n", Status);
Status= RpcServerUnregisterIf(NULL, NULL, FALSE);
if ( Status!=RPC_S_OK )
wprintf(L"RpcServerUnregisterIf failed (0x%08x)\n", Status);
exit(Status);
}
return 0;
}
5. RPC クライアントを書く
次に RPC クライアントを書きます。こちらも単一ファイルで。
サーバーと同じく、midl_user_allocate と midl_user_free の定義と、rpcrt4.lib のリンカへの追加を忘れないように。
//
// pipoclient.cpp
//
#include <Windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Rpc.h>
#include "pipo.h"
#define PROT_LPC ((RPC_WSTR)L"ncalrpc")
#define PROT_NP ((RPC_WSTR)L"ncacn_np")
enum METHODTYPE {
method_Shutdown,
method_Sleep,
method_Hello,
method_EOL // End-Of-List
};
#define MAX_METHODNAME 16
struct METHOD {
METHODTYPE Type;
WCHAR Name[MAX_METHODNAME];
int MinParameter;
};
const METHOD Methods[]= {
{method_Shutdown, L"SHUTDOWN", 4},
{method_Sleep, L"SLEEP", 5},
{method_Hello, L"HELLO", 5},
{method_EOL, L"", 0}
};
/*
usage: pipoclient [PIPE|LPC] [endpoint] [option]
shutdown
shutdown RPC server
sleep [duration]
sleep
hello [message]
show message
*/
void ShowUsage() {
wprintf(L"usage: pipoclient [PIPE|LPC] [endpoint] [method] [option]\n");
wprintf(L" shutdown\n");
wprintf(L" shutdown RPC server\n");
wprintf(L" sleep [duration]\n");
wprintf(L" sleep\n");
wprintf(L" hello [message]\n");
wprintf(L" show message\n");
}
static wchar_t upperstr[MAX_METHODNAME+1];
wchar_t *ToUpper(const wchar_t *s) {
for ( int i=0 ; i<MAX_METHODNAME+1 ; ++i ) {
upperstr[i]= toupper(s[i]);
if ( s[i]==0 )
return upperstr;
}
upperstr[MAX_METHODNAME]= 0;
return upperstr;
}
int wmain(int argc, wchar_t *argv[]) {
if ( argc<4 ) {
ShowUsage();
return ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER;
}
LPWSTR UpperString= NULL;
RPC_WSTR Protocol= NULL;
UpperString= ToUpper(argv[1]);
if ( wcscmp(UpperString, L"PIPE")==0 )
Protocol= PROT_NP;
else if ( wcscmp(UpperString, L"LPC")==0 )
Protocol= PROT_LPC;
else {
ShowUsage();
wprintf(L"Unknown procotol.\n");
return ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER;
}
UpperString= ToUpper(argv[3]);
int MethodIndex= -1;
for ( int i=0 ; Methods[i].Type!=method_EOL ; ++i ) {
if ( wcscmp(Methods[i].Name, UpperString)==0 ) {
MethodIndex= i;
break;
}
}
if ( MethodIndex<0 || argc<Methods[MethodIndex].MinParameter ) {
ShowUsage();
wprintf(L"Bad parameter.\n");
return ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER;
}
RPC_STATUS Status= RPC_S_OK;
RPC_WSTR Binding= NULL;
Status= RpcStringBindingCompose(
NULL, Protocol, NULL, (RPC_WSTR)argv[2], NULL, &Binding);
if (Status!=RPC_S_OK) {
wprintf(L"RpcStringBindingCompose failed (0x%08x)\n", Status);
return Status;
}
Status= RpcBindingFromStringBinding(Binding, &pipo_IfHandle);
if (Status!=RPC_S_OK) {
wprintf(L"RpcBindingFromStringBinding failed (0x%08x)\n", Status);
return Status;
}
RpcTryExcept {
wprintf(L"%s is invoked.\n", Methods[MethodIndex].Name);
switch ( Methods[MethodIndex].Type ) {
case method_Shutdown:
Shutdown();
break;
case method_Hello:
Hello(argv[4]);
break;
case method_Sleep:
RpcSleep(_wtoi(argv[4]));
break;
}
}
RpcExcept( EXCEPTION_EXECUTE_HANDLER ) {
printf("Caught exception: 0x%08x\n", RpcExceptionCode());
}
RpcEndExcept
Status = RpcStringFree(&Binding);
if (Status!=RPC_S_OK)
wprintf(L"RpcStringFree failed (0x%08x)\n", Status);
Status= RpcBindingFree(&pipo_IfHandle);
if (Status!=RPC_S_OK)
wprintf(L"RpcBindingFree failed (0x%08x)\n", Status);
return 0;
}
void __RPC_FAR * __RPC_API midl_user_allocate(size_t len) {
return malloc(len);
}
void __RPC_API midl_user_free(void __RPC_FAR * ptr) {
free(ptr);
}
6. とりあえず動かす
せっかくなので動かしてみましょう。
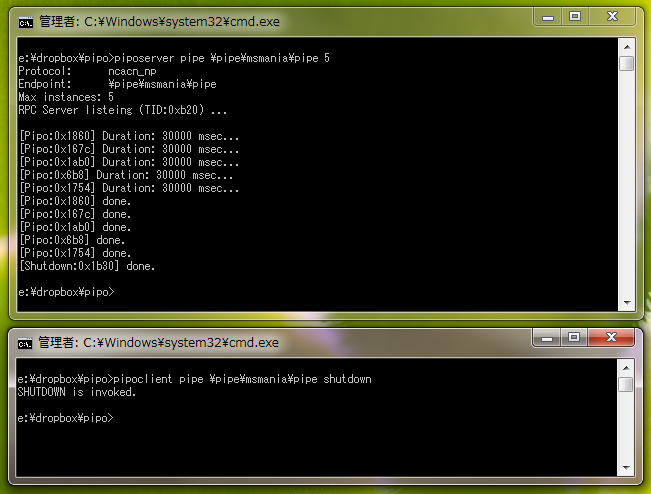
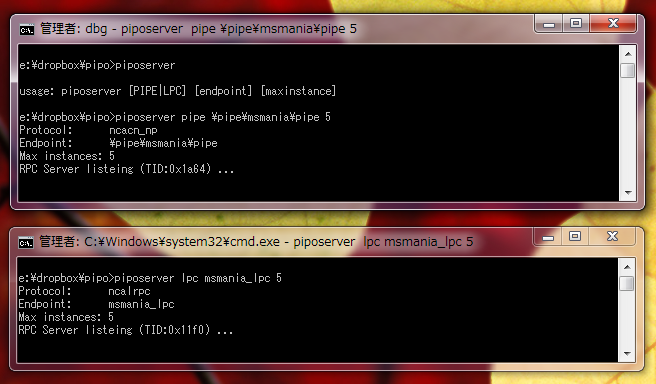
まずは、RPC サーバーを起動します。パイプは \pipe\パイプ名 という名前じゃないと RPC_S_INVALID_ENDPOINT_FORMAT エラーになるので注意。LPC ポート名も、円記号などを含めると同じエラーが発生します。
実際にパイプや LPC ポートが作られたかどうかは、Sysinternals ツールで調べることができます。
Sysinternals Suite は便利なので、必ずダウンロードしておきましょう。
http://technet.microsoft.com/ja-jp/sysinternals/bb842062
名前付きパイプは、pipelist.exe で一覧を見ることができます。(結果は一部抜粋)
e:\dropbox\pipo> pipelist
PipeList v1.01
by Mark Russinovich
http://www.sysinternals.com
Pipe Name Instances Max Instances
--------- --------- -------------
InitShutdown 3 -1
lsass 4 -1
protected_storage 3 -1
ntsvcs 3 -1
scerpc 3 -1
plugplay 3 -1
epmapper 3 -1
LSM_API_service 3 -1
ExtEventPipe_Service 1 30
eventlog 3 -1
Winsock2\CatalogChangeListener-80-0 1 1
atsvc 3 -1
wkssvc 4 -1
msmania\pipe 3 -1
ちなみに同じパイプ名でサーバーを起動してもエラーになることはなく、インスタンスが 3 から 6 になりました。
LPC ポートは Winobj.exe から見ることができます。RPC Control のところにあります。
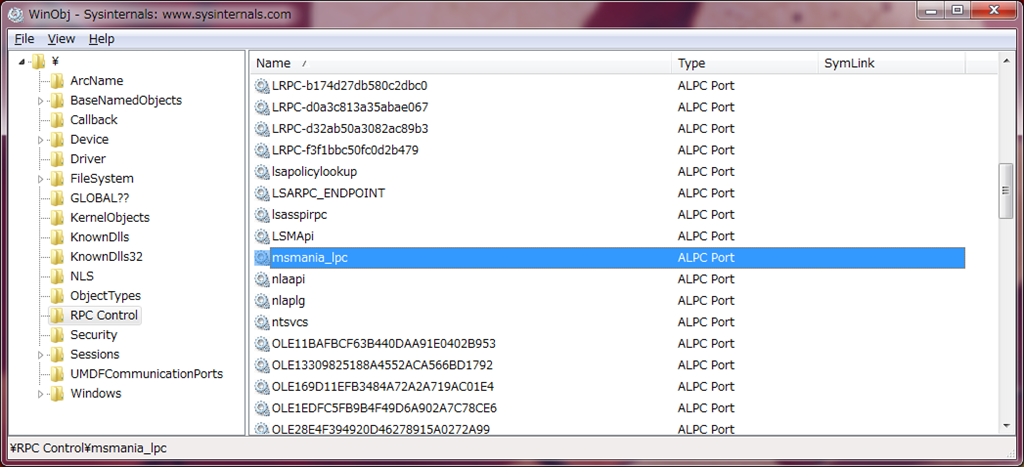
LPC ポートの場合は、同じポート名でサーバーの起動を試みると、RPC_S_DUPLICATE_ENDPOINT エラーが発生します。
この状態で、次に RPC クライアントを実行します。
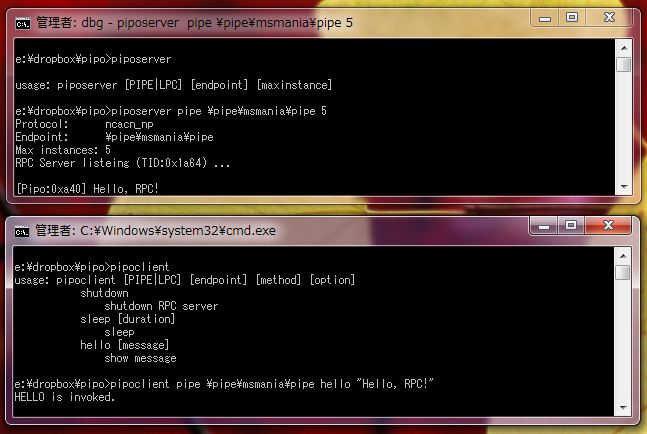
何回かメソッドを呼ぶと、スレッドが切り替わる様子も確認できます。
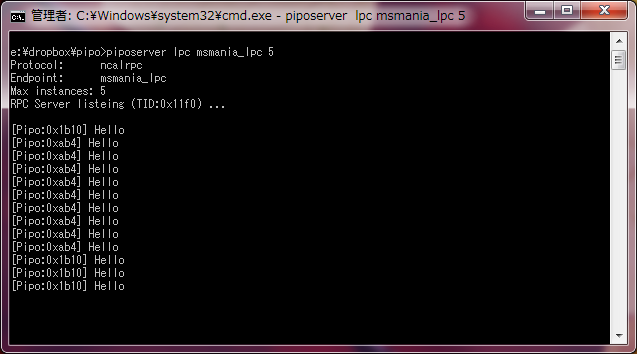
RPC サーバーを起動するときに最大インスタンス数を 5 に設定しましたので、5 セッションを枯渇させると RPC_S_SERVER_TOO_BUSY (0x000006bb) エラーが発生します。
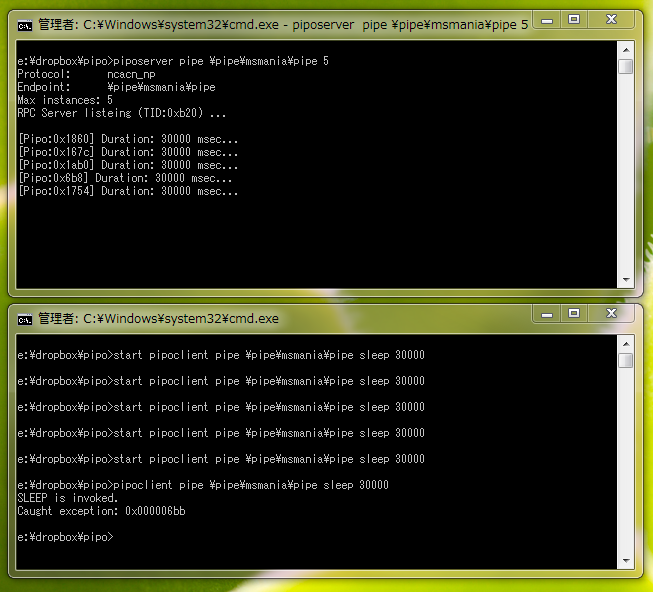
他にも、RPC エラーを発生させるパターンはいろいろ考えられるので、簡単に確認できるツールがあると便利です。
遊び終わったら、Shutdown メソッドでも呼んでおきます。